Health Library
We have a vast digital library of medical information, including wellness and psychiatry topics as well as general medical topics. For more information or to schedule an appointment, don’t hesitate to call us.
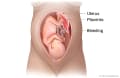
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein. Placental abruption is a pregnancy problem in which the placenta separates too early from the wall of the uterus. The placenta is a round, flat organ that forms during pregnancy. It gives the baby food and oxygen from your body. Placental abruption can be very harmful. In rare cases, it can be deadly. Placental abruption usually occurs in the third trimester. But it can happen at any time after the 20th week of pregnancy. Doctors aren't sure what causes it, but some things can raise your risk. These are called risk factors. Common risk factors for placental abruption include: Less common risk factors include: If you have placental abruption, you may notice one or more warning signs. Call your doctor right away if you are pregnant and you: You can't really tell how serious placental abruption is by the amount of vaginal bleeding. Sometimes the blood gets trapped between the placenta and the wall of the uterus. So there might be a serious problem even if there is only a little bleeding. More serious symptoms include: In rare cases, symptoms of shock are the only signs of a serious problem. This problem can be hard to diagnose. Your doctor will ask questions about your symptoms and do a physical exam. Tests that may be done include: If placental abruption is suspected, you'll probably need to be in the hospital until your doctor finds out how severe it is. The kind of treatment you need will depend on: If you have mild placental abruption and your baby is not in distress, you may not have to stay in the hospital. If you have moderate to severe placental abruption, you will probably have to stay in the hospital so your baby's health can be watched closely. If your baby is premature, the baby may be treated in a neonatal intensive care unit, or NICU. The NICU is geared to the needs of premature or ill newborns. There is no sure way to prevent placental abruption, but you can do things to lower your risk. Your risk is much higher than normal if you have had placental abruption before, so these steps are very important. Current as of: July 15, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Current as of: July 15, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Clinical Review Board This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content. To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com. © 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.Topic Contents
Placental Abruption
Condition Basics
What is placental abruption?
What causes it?
What are the symptoms?
How is it diagnosed?
How is placental abruption treated?
Can you prevent it?
Related Information
Credits
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.