Health Library
We have a vast digital library of medical information, including wellness and psychiatry topics as well as general medical topics. For more information or to schedule an appointment, don’t hesitate to call us.
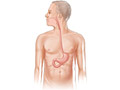
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein. A HIDA scan is an imaging test that checks how your gallbladder is working. The gallbladder is a small sac under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid that helps your body digest fats. If there are problems with the gallbladder, such as gallstones, the gallbladder may not store or empty bile properly. During a HIDA scan, a camera takes pictures of your gallbladder after a radioactive tracer is injected into a vein in your arm. The tracer travels through your liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and small intestine. The camera takes a series of pictures of the tracer as it moves along. Your doctor can use these pictures to look for leaks, blockages, or any other problems. The HIDA scan may be done to: A HIDA scan is sometimes done if an earlier ultrasound test did not give enough information. You will need to take off any jewelry that might affect the scan. You may need to take off all or most of your clothes. This depends on which part of your body is being examined. You may be allowed to keep on your underwear if it does not affect the test. You will be given a cloth or paper covering to use during the test. The site on your arm where the radioactive tracer goes in will be cleaned. A small amount of the tracer is then injected. You will lie on your back on a table. A large scanning camera will be placed just above your belly. After the radioactive tracer is injected, the camera will scan for radiation released by the tracer. The camera makes pictures as the tracer passes through your liver and into your gallbladder and small intestine. The first pictures will be taken right after the tracer starts to go in. The pictures may be continuous, like a video. Or they may be taken once in a while for up to 1½ hours after the test starts. Each scan takes only a few minutes. You need to lie very still during each scan so the pictures won't be blurred. The camera does not produce any radiation. So you are not exposed to any more radiation while the scan is being done. A substance that stimulates the gallbladder may also be put into your vein during the scans. The pictures taken after this injection can help see if the gallbladder is working normally. A computer may look at the data to check how well the gallbladder is working. You may be asked about your reaction to the substance used to stimulate the gallbladder. Sometimes medicine (morphine sulfate) is given to help find out if the gallbladder is inflamed. A HIDA scan takes about 1 to 2 hours. You may feel nothing at all from the needle, or you may feel a brief sting or pinch. Otherwise, a HIDA scan usually doesn't hurt. You may find it hard to stay still during the scan. Ask for a pillow or a blanket to get as comfortable as you can before the scan starts. The test may be uncomfortable if you are having pain in your belly. Try to relax by breathing slowly and deeply. You may have nausea or belly pain if a substance that stimulates the gallbladder is used during the test. You may be asked about changes in your pain during the test. Allergic reactions to the radioactive tracer are rare. Some people may have soreness or swelling where the needle went in. These symptoms can usually be relieved by putting moist, warm compresses on your arm. Anytime you're exposed to radiation, there's a small chance of damage to cells or tissue. That's the case even with the low-level radioactive tracer used for this test. But the chance of damage is very low compared with the benefits of the test. The results of a HIDA scan are ready in 2 days. Normal: The radioactive tracer flows evenly through the liver and then into the gallbladder and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). The gallbladder is normal in size, shape, and location. Abnormal: The tracer may not be removed normally from the blood by the liver. This may be a sign of liver disease. The gallbladder does not contract or empty normally. The tracer may not reach the gallbladder. This means that there is swelling or that the duct is blocked by a gallstone. The tracer may not reach the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). This may mean that a bile duct is blocked by a stone. Or there may be a tumor, infection, or swelling of the pancreas. Pain occurs when the gallbladder empties the tracer. Current as of: March 26, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Current as of: March 26, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Clinical Review Board This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content. To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com. © 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.HIDA Scan
Test Overview
Why It Is Done
How To Prepare
How It Is Done
During the test
How long the test takes
How It Feels
Risks
Steps you can take
Results
Related Information
Credits
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.