Health Library
We have a vast digital library of medical information, including wellness and psychiatry topics as well as general medical topics. For more information or to schedule an appointment, don’t hesitate to call us.
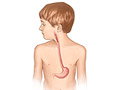
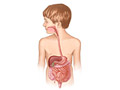
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein. Gastroesophageal reflux is a backflow (reflux or regurgitation) of food and stomach acid into the esophagus. This is the tube that connects the throat to the stomach. When reflux irritates the lining of the esophagus and causes burning pain, difficulty eating, weight loss, or other problems, it is called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Reflux is common in babies and children. It's most often not a sign of a serious problem. Most babies stop having reflux around 1 year of age. A child who continues to have reflux may need treatment. Gastroesophageal reflux happens because of a problem with the ring of muscle at the end of the esophagus. The ring of muscle is called the lower esophageal sphincter. It acts like a one-way valve between the esophagus and the stomach. When your child swallows, the valve lets food pass into the stomach. If the valve is weak, stomach contents can flow back up into the esophagus. In babies, this problem happens because the digestive tract is still growing. Reflux usually goes away as a baby matures. It is common for babies to spit up (have reflux) after they eat. Babies with severe gastroesophageal reflux may cry, act fussy, or have trouble eating. They may not sleep well or grow as expected. An older child or teen may have the same symptoms as an adult. They may cough a lot and have a burning feeling in the chest and throat (heartburn). They may have a sour or bitter taste in the mouth. If stomach acid goes up to the throat or into the airways, a child may get hoarse or have a lasting cough. Reflux can also cause pneumonia or wheezing, and it may hurt to swallow. Gastroesophageal reflux is a backflow (reflux or regurgitation) of food and stomach acid into the esophagus, which is the tube that connects the throat to the stomach. To find out if a child has gastroesophageal reflux, a doctor will do a physical exam and ask about symptoms. Tests are not usually needed. But sometimes they are recommended when your doctor is worried that something other than gastroesophageal reflux is causing symptoms. Or they might be needed if your child has other symptoms like coughing. Tests can include: Most babies stop having gastroesophageal reflux over time, so the doctor may just suggest that you follow some steps to help reduce the problem until it goes away. For example, it may help to: For older children and teens, it may help to: If these steps don't work, the doctor may suggest medicine. Medicines that may be used include: Children with reflux rarely need surgery. Current as of: October 24, 2024 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Current as of: October 24, 2024 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Clinical Review Board This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content. To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com. © 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.Topic Contents
Gastroesophageal Reflux in Babies and Children
Condition Basics
What is gastroesophageal reflux in babies and children?
What causes it?
What are the symptoms?
How is it diagnosed?
How is gastroesophageal reflux treated in babies and children?
Related Information
Credits
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.