Condition Basics
What is diverticulosis?
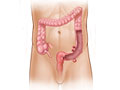
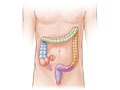
Diverticulosis is a condition that develops when pouches (diverticula) form in the wall of the colon (large intestine). These pouches are usually very small (5 to 10 millimeters) in diameter. But they can be larger.
In diverticulosis, the pouches in the colon wall don't cause symptoms. The condition may not be found unless symptoms occur, such as in painful diverticular disease or in diverticulitis. Most people who have diverticulosis never get diverticulitis. In many cases, diverticulosis is discovered only when tests are done to find the cause of a different medical problem or during a screening exam.
What causes it?
The reason pouches (diverticula) form in the colon wall is not completely understood. Doctors think diverticula form when high pressure inside the colon pushes against weak spots in the colon wall.
Normally, a diet with adequate fiber produces stool that is bulky and can move easily through the colon. A low-fiber diet can cause small, hard stools. This means it takes more pressure in the colon to move stools out of the body. This puts more pressure on the walls of the colon. A low-fiber diet also can increase the time stool remains in the bowel, adding to the high pressure.
Pouches may form when the high pressure pushes against weak spots in the colon where blood vessels pass through the muscle layer of the bowel wall to supply blood to the inner wall.
What are the symptoms?
Most people don't have symptoms. You may have had diverticulosis for years by the time symptoms occur (if they do). Over time, some people get an infection in the pouches (diverticulitis). The pouches sometimes bleed.
How is it diagnosed?
In many cases, diverticulosis is discovered only when tests, such as a barium enema X-ray, a colonoscopy, or a CT scan are done to find the cause of a different medical problem or during a screening exam.
How is diverticulosis treated?
The best way to treat diverticulosis is to avoid constipation. Here are some ideas:
- Include fruits, vegetables, beans, and whole grains in your diet each day. These foods are high in fiber.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Get some exercise every day. Try to do moderate activity that adds up to at least 2½ hours a week. Or try to do vigorous activity that adds up to at least 1¼ hours a week.
- Take a fiber supplement, such as Citrucel or Metamucil, every day if needed. Read and follow all instructions on the label.
- Schedule time each day for a bowel movement. Having a daily routine may help. Take your time and do not strain when you are having a bowel movement.
This treatment may help reduce the formation of new pouches (diverticula) and lower the risk for diverticulitis.
How can you prevent it?
Eating a high-fiber diet, getting plenty of fluids, and exercising regularly may help prevent diverticulosis.