Health Library
We have a vast digital library of medical information, including wellness and psychiatry topics as well as general medical topics. For more information or to schedule an appointment, don’t hesitate to call us.
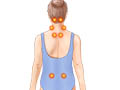
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein. Fibromyalgia is a condition that causes widespread pain in the muscles and soft tissues. This pain is felt above and below the waist and on both sides of the body. People with fibromyalgia feel pain, tenderness, or both even when there is no injury or inflammation. The pain can be long-lasting (chronic). But fibromyalgia isn't life-threatening, and it doesn't damage the muscles, joints, or internal organs. Fibromyalgia is a syndrome or a set of symptoms that occur together. It has no cure. When it's not controlled, you may not have any energy. Or you may feel depressed or have trouble sleeping. But with treatment, most people with fibromyalgia are able to work and do their regular activities. No one knows for sure what causes fibromyalgia. But experts have some ideas. For example, nerve cells may be too sensitive. Or chemicals in the brain (neurotransmitters) may be out of balance. The main symptoms of fibromyalgia are a deep or burning pain in your trunk, neck, low back, hips, and shoulders, and tender points on the body that hurt when pressed. Some people have other problems, such as fatigue, sleep problems, and depression. Symptoms tend to come and go. There are no specific tests for fibromyalgia. You'll probably have lab tests to make sure that you don't have another condition that causes pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus. Doctors diagnose fibromyalgia by using a set of guidelines to assess the pattern of pain and other symptoms. Treatment is focused on managing pain, fatigue, depression, and other symptoms common in fibromyalgia. The goal is to break the cycle of increased sensitivity to pain and decreased physical activity. You may be able to control your symptoms by: This is one of the best ways to manage the pain. Medicines may help you sleep better, relax your muscles, or relieve muscle and joint pain. This can help you cope with long-term (chronic) pain. Good self-care includes finding better ways to handle stress, having good sleep habits, and talking to your doctor if you have symptoms of depression. Some people with fibromyalgia also find complementary therapies helpful. These include tai chi, behavioral therapy, and relaxation techniques. Finding the right treatment can take time. You may have to try several different treatments to find an approach that works for you. Health Tools help you make wise health decisions or take action to improve your health. No one knows for sure what causes fibromyalgia. But experts have some ideas, such as: Many people connect the start of their symptoms to a certain event. Examples include the flu, an injury or surgery, or emotional trauma and stress. An event of this type combined with other things, such as being more sensitive to pain, may lead to fibromyalgia in some people. Certain things may make you more likely to have fibromyalgia. Things that increase your risk (risk factors) include: The main symptoms of fibromyalgia are: People with fibromyalgia may have other problems along with pain, such as: Symptoms tend to come and go. You may have times when you hurt more, followed by times when symptoms happen less often, are milder, or are absent (remission). Some people find that their symptoms are worse in cold and damp weather, during times of stress, or when they try to do too much. For most people, fibromyalgia seems to involve a cycle of muscle pain, increased sensitivity to pain, and inactivity that may be made worse by sleep problems and fatigue. Fibromyalgia is a long-lasting (chronic) condition with no cure, but it can be controlled. It doesn't damage the muscles, joints, or internal organs. Most people adjust to their symptoms and can keep working and doing daily activities. Call your doctor if you've had the following symptoms for several weeks without an obvious cause. They may be signs of fibromyalgia, especially if they have developed gradually. If you have fibromyalgia, call your doctor if you have: Health professionals who may be able to help you with fibromyalgia include: You may need to see a specialist who has experience with fibromyalgia. These include: Pain management programs can be helpful too. These typically include a team of doctors, counselors, physical therapists, nurses, and pharmacists who can help you develop a strategy for pain management. Your personal program may include medicines, complementary therapies, diet, exercise, and counseling. There are no specific tests for fibromyalgia. You'll probably have lab tests to make sure that you don't have another condition that causes pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus. Your doctor will also ask questions about your medical history and do a physical exam. Doctors use a set of guidelines to diagnose fibromyalgia. You may be diagnosed with fibromyalgia if you have: Fibromyalgia is sometimes diagnosed or described using pain and tenderness at 18 specific spots on the body. These spots are called tender points or trigger points. Treatment is focused on managing pain, fatigue, depression, and other symptoms common in fibromyalgia. The goal is to break the cycle of increased sensitivity to pain and decreased physical activity. There are many steps you can take to manage your symptoms. The treatment you need or want may be based on: Because the symptoms of fibromyalgia can come and go, you may find it hard to judge whether a certain treatment is really working. Different people may respond differently to each type of treatment. Many people with fibromyalgia have other joint or muscle diseases (such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus) that need to be treated too. Try to be patient. Finding the right treatment can take time. You may have to try several different treatments to find an approach that works for you. Getting regular exercise, especially cardiovascular exercise, is one of the best ways to manage fibromyalgia. Pool exercise, like water aerobics or swimming, is a good example. It's important to build up your exercise program slowly so you don't get sore muscles that cause you to want to stop exercising. Working with a physical therapist familiar with fibromyalgia may be helpful. Medicines are part of the long-term treatment of fibromyalgia. They may help you sleep better, relax your muscles, or relieve muscle and joint pain. Your doctor may suggest prescription medicines, such as antidepressants, muscle relaxants, and anticonvulsants. Or your doctor may suggest nonprescription pain relievers. Not all people with fibromyalgia will need, want, or benefit from medicines. You might need to try more than one medicine before you find one that works best for you. You may also find that a medicine that has been helping your symptoms seems to not work as well over time. Cognitive behavioral therapy and other forms of counseling, including relaxation therapy and biofeedback, can help people who have fibromyalgia. Counseling can help with the pain of fibromyalgia. It can also help with sleep problems and fatigue. And it may improve your mood. Taking care of yourself is an important part of managing fibromyalgia. For example, you can: With help, you can start working on most of these goals at home. You may have a team of health professionals to help you. Home treatment is the most important part of treating fibromyalgia. There are many things you can do over time to treat your symptoms. Of all the treatments for fibromyalgia, cardiovascular (aerobic) exercise may have the most benefit in reducing pain and other symptoms and in improving your overall condition. Work with a physical therapist or other professional who has expertise with fibromyalgia to build an exercise program that works for you. And then stay with it. Common triggers include cold or damp weather, poor sleep, fatigue, physical or emotional stress, and being too active. Sleep disturbances seem to both cause and result from some of the other symptoms of fibromyalgia, such as pain. Learn good sleep habits. And try to get enough sleep each night. Heat therapy, massage, gentle exercise, and short-term use of nonprescription pain relievers may be helpful. Finding healthy ways to cope with stress may help reduce your pain. The more you know about fibromyalgia, the more control you will have over your symptoms. People who feel more in control also tend to be more active and report less pain and other symptoms. Feeling as though you are not thinking clearly—sometimes called "fibro fog"—increases stress and can make memory problems worse. Simple things like writing yourself notes can help you feel more in control. It's hard to stay positive when you don't feel well. But a good attitude helps you focus less on your challenges and feel more healthy. The best results occur when you take an active, committed role in your own treatment. You may need to adjust your lifestyle to fit home treatment, especially regular exercise, into your daily routine. It may take time to find an approach that works for you. Try to be patient. And keep in mind that consistent home treatment usually can help relieve or control symptoms of fibromyalgia. Medicines are often part of the long-term treatment of fibromyalgia. They may help when symptoms flare up. But not all people with fibromyalgia will benefit from medicines. Medicines may be used to improve sleep, relieve pain and fatigue, and (in some cases) treat depression. These improvements in symptoms may allow you to feel better and to be more active. Medicines used for fibromyalgia include: Tramadol (Ultram) is sometimes used for pain. Sometimes it is combined with acetaminophen. Your doctor may try more than one medicine before finding one that works best for your symptoms. Sometimes a medicine that has been helping your symptoms doesn't seem to work as well over time. Talk with your doctor if you aren't getting relief. The pain and other symptoms of fibromyalgia can get worse during stressful times. The good news is that there are a lot of things you can do to lower your stress. For example, research shows that you can change how you think. And how you think affects how you feel. Here are some techniques you can try on your own or with help from a therapist or counselor trained in muscle relaxation, meditation, biofeedback, or cognitive behavioral therapy: Complementary treatments that have been used to treat fibromyalgia include: Most mind and body practices—such as acupuncture, tai chi, and yoga—are safe when used under the care of a well-trained professional. Choose an instructor or practitioner as carefully as you would choose a doctor. Talk with your doctor about the safety and potential side effects of the treatment. Remember that fibromyalgia doesn't physically harm you or damage your body. A treatment that could be harmful may not be worth the risk, especially when its benefits are unproven. Avoid treatments that may be harmful, such as unusual diets or excessive vitamin or mineral supplements. (A daily multiple vitamin-mineral supplement is okay. Try to avoid taking more than 100% of the recommended dietary allowance for any vitamin or mineral unless your doctor prescribes a special supplement.) Current as of: July 24, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Current as of: July 24, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Clinical Review Board This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content. To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com. © 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.Fibromyalgia
Condition Basics
What is fibromyalgia?
What causes it?
What are the symptoms?
How is it diagnosed?
How is fibromyalgia treated?
Health Tools
Cause
What Increases Your Risk
Symptoms
What Happens
When to Call a Doctor
If not diagnosed
If diagnosed
Who to see
Exams and Tests
Learn more
Treatment Overview
Exercise
Medicines
Counseling
Self-care
Learn more
Self-Care
Learn more
Medicines
Learn more
Other Treatment
Cognitive techniques and stress management
Complementary treatments
Learn more
Related Information
Credits
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.